
Restricted retained earnings are portions of a company’s retained earnings that are not available for dividend distribution due to legal or contractual obligations. These restrictions ensure that certain financial covenants or future expenditures are adequately funded. The figure is calculated at the end of each accounting period (monthly, quarterly, or annually). As the formula suggests, retained earnings are dependent on the corresponding figure of the previous term. The resultant number may be either positive or negative, depending on the net income or loss generated by the company over time. Alternatively, the company paying large dividends that exceed the other figures can also lead to the retained earnings going negative.

Key Terms
However, it can be challenged by the shareholders through a majority vote, as they are the actual owners of the company. All of the other options retain the earnings for use within the business, and such investments and funding activities constitute retained earnings. My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers. Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
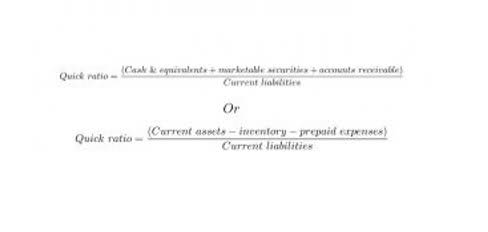
- For example, a loan contract may state that part of a corporation’s $100,000 of retained earnings is not available for cash dividends until the loan is paid.
- This is the least liquid of unrestricted net assets and is not required.• Net assets with donor restrictions can be time, purpose, or permanently restricted (i.e., endowment).
- A summary report called a statement of retained earnings is also maintained, outlining the changes in RE for a specific period.
- In Canada, these restrictions are primarily governed by corporate laws and securities regulations.
- Such appropriation is voluntary by dividing the retained earnings into various headings, denoting the use for which appropriation has been made.
- They reflect the profits that have been reinvested in the business or used to pay down debt, rather than being paid out as dividends.
Accounting Alert
Retained earnings are a type of equity and are therefore reported in the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet. Although retained earnings are not themselves an asset, they can be how to calculate retained earnings used to purchase assets such as inventory, equipment, or other investments. Therefore, a company with a large retained earnings balance may be well-positioned to purchase new assets in the future or offer increased dividend payments to its shareholders.
- In general, you can expect your shares to be worth a specific amount if you are not required to pay them.
- Also, mistakes corrected in the same year they occur are not prior period adjustments.
- In the accompanying notes, there would be an explanation that the $200,000 in restricted retained earnings is due to loan covenants, legal requirements, or any other relevant reasons.
- This calculation reflects the cumulative nature of retained earnings, showing how profits are accumulated over time.
- To prepare this entry, you will need to determine what the new ending balances need to be.
- If a company were to go bankrupt, the appropriated amounts would return to the main retained earnings account and would be available to creditors and shareholders.
BAR CPA Practice Questions: Budgetary Comparison Reporting
Retained earnings are funds reserved by a company’s board of directors or management for specific purposes. Companies can’t distribute these funds to shareholders, but the board of directors can decide to set Bookkeeping for Startups aside a portion of them for certain purposes. Retained earnings can typically be found on a company’s balance sheet in the shareholders’ equity section. Retained earnings are calculated by taking the beginning-period retained earnings, adding the net income (or loss), and subtracting dividend payouts.
- The retained earnings portion of stockholders’ equity typically results from accumulated earnings, reduced by net losses and dividends.
- Observing it over a period of time (for example, over five years) only indicates the trend of how much money a company is adding to retained earnings.
- Companies must adhere to accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS to ensure consistency and clarity.
- Instead, companies mention any such amount in the footnotes to the financial statements.
Stock Dividend Impacting Retained Earnings
Generally, retained earnings is listed as a single shareholder’s equity account on the https://www.bookstime.com/ balance sheet. For instance, if management sets aside funds for plant expansion or regulatory compliance, it signals a commitment to future growth rather than short-term returns. While appropriated retained earnings are set aside for specific purposes, these designations are not permanent. A company may reverse an appropriation if the intended project is canceled, completed under budget, or if management determines that the restriction is no longer necessary. Shareholder distributions, also known as dividends, represent money paid to stockholders periodically throughout the year. However, management must balance dividend payouts with the need to retain funds for future investments and stability.

